doi: 10.56294/dm2023231
ORIGINAL
Strategic planning and organizational culture
Planificación estratégica y cultura organizacional
Ana Chaman-Bardalez1 ![]() *, Alberto Ramón-Osorio1
*, Alberto Ramón-Osorio1 ![]() *, Segundo Ríos-Ríos1
*, Segundo Ríos-Ríos1 ![]() *, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco1
*, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco1 ![]() *, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez1
*, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez1 ![]() *
*
1Universidad Nacional de Cañete, Facultad de Administración de Empresas. Ica, Perú.
Cite as: Chaman-Bardalez A, Ramón-Osorio A, Ríos-Ríos S, Vargas-Tasayco M, Uribe-Hernandez Y. Strategic planning and organizational culture. Data and Metadata. 2023;2:231. https://doi.org/10.56294/dm2023231
Submitted: 22-09-2023 Revised: 31-11-2023 Accepted: 29-12-2023 Published: 30-12-2023
Editor: Prof.
Dr. Javier González Argote ![]()
ABSTRACT
Introduction: The thesis “Strategic planning and organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021” highlights that strategic planning is a structured process through which an organization considers where it wants to go and how it is going to achieve it. Likewise, organizational culture is that culture (set of values, beliefs, and other representative characteristics of a group of people) that are reflected within an organization and that identify it as such.
Objective: Determine how strategic planning is associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Method: Research with a quantitative approach, basic type, non-experimental cross-sectional design, and correlational level. The population was made up of 10 people from the company and the research sample was made up of the entire population. Two surveys were used: strategic planning and organizational culture, composed of 28 and 60 questions for each instrument, respectively, which were validated by expert judgment and reliability through Cronbach’s alpha, respecting ethical considerations.
Results: The results obtained consider that strategic planning is significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, because Spearman’s Rho statistical test is 0,764, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered a very strong positive correlation. In relation to the dimensions: involvement, consistency, adaptability, and mission, with strategic planning it was found that they have a significant association.
Conclusions: In conclusion, there is an association between both variables. Therefore, the implementation of strategic planning in micro and small businesses (MYPE) establishes the procedure to follow and the appropriate organizational culture contributes to the fulfillment of what is planned, allowing the continuous improvement of the company and the scope of business success.
Keywords: Strategic planning; Organizational culture; MYPE.
RESUMEN
Introducción: La tesis “Planificación estratégica y cultura organizacional de la Bodega y Viñedos Santa María SAC del distrito de Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021”, destaca que la planificación estratégica es un proceso estructurado mediante el cual una organización considera hacia dónde quiere llegar y cómo va a alcanzarlo. Asimismo, la cultura organizacional es aquella cultura (conjunto de valores, creencias y otras características representativas de un grupo de personas) que se reflejan dentro de una organización y que la identifican como tal.
Objetivo: Determinar cómo se asocia la planificación estratégica con la cultura organizacional de Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. del distrito de Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Método: Investigación con enfoque cuantitativo, tipo básico, diseño transversal no experimental y nivel correlacional. La población estuvo conformada por 10 personas de la empresa y la muestra de investigación estuvo compuesta por toda la población. Se utilizaron dos encuestas: planificación estratégica y cultura organizacional, compuestas por 28 y 60 preguntas para cada instrumento, respectivamente, las cuales fueron validadas por juicio de expertos y confiabilidad a través del alfa de Cronbach, respetando consideraciones éticas.
Resultados: Los resultados obtenidos consideran que la planificación estratégica está asociada significativamente con la cultura organizacional de Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. del distrito de Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, debido a que la prueba estadística Rho de Spearman es de 0,764, la cual según la tabla de análisis de correlación se considera una correlación positiva muy fuerte. En relación con las dimensiones: involucramiento, consistencia, adaptabilidad y misión, con la planificación estratégica se encontró que tienen una asociación significativa.
Conclusiones: En conclusión, existe una asociación entre ambas variables. Por lo tanto, la implementación de la planificación estratégica en las micro y pequeñas empresas (MYPE), establece el procedimiento a seguir y la cultura organizacional adecuada contribuye al cumplimiento de lo planificado, permitiendo la mejora continua de la empresa y los alcances del éxito empresarial.
Palabras clave: Planificación Estratégica; Cultura organizacional; MYPE.
INTRODUCTION
Micro and small enterprises are an important factor in the economy and are the largest source of employment. These economic units that are united under a concept, as mentioned in his book The world of small business Villarán de la Puente(1) "The first attempts to prevent the deepening of the distances between both worlds (that of SMEs and microenterprises) took place in the 90s by bringing together micro with small companies, emerging the concept of MSE" (p.29), extend in all existing economic sectors.
At the global level, the representation that micro and small enterprises have in the economy of each country for their contribution to employment and national Gross domestic product (GDP) cannot be ignored, however, most of them present difficulties to remain current in the market.
In Colombia, for example, a research team from the School of Business Administration of the Externado de Colombia University, over two years, has studied the main problems that afflict small and medium-sized enterprises in their country.
In this way, the study is based on twenty common problems of a strategic and operational nature that affect the competitive level of the 52 companies analyzed, of which the lack of a strategic plan that allows the company to set both corporate objectives and for each of its areas to develop a managerial management of the medium and long term.(2)
In Nicaragua, research addresses the situation of small and medium-sized enterprises, from a strategic approach in a globalized world, where we can identify that entrepreneurs face, among others, problems in management, which makes it difficult to design long-term strategies.
Therefore, to know the strategy to follow, Cuadra(3) in its research work "Nicaragua, strategic approach of SMEs in a globalized world" says:
It is necessary to analyze their current situation; Next, you must define what you want your situation to be in the future and make that aspiration the main engine of the activity. It is not about making complicated analyses, but about generating a motivation capable of anticipating the future including a living and evolving image of where we want to be in 5 or 10 years. That motivation created by the employer must be attractive enough to be shared by the rest of the staff, so that it convinces and excites him as much as his creator, commits to it and becomes the guide of daily work.
In Ecuador, a study on the impact of COVID-19 on the strategic planning of Ecuadorian SMEs, brings to light the problems that have been generated by this disease, and how precisely in circumstances like this, it is where strategic planning can make the difference between the success or failure of a company.
Huilcapi Masacón et al. mentioned that: "Based on what has been found in this review, it is undoubted to deduce that, for the successful exercise of any organization, strategic planning is fundamental, since this process will mean the way on which the functions of the company will begin".(4)
At the national level, MSEs have an important presence in Peru, since they boost the national economy and contribute a lot to it due to their great concentration. In that sense, the newspaper Gestión mentions that "According to the National Institute of Statistics and Informatics, INEI in Peru there are 2 million 332 thousand 218 companies of which more than 95 % are in the MSE regime."(5)
These companies currently need to face great challenges, one of them is to increase their competitiveness, which will allow them to obtain benefits and guarantee their permanence in the market. This leads us to think that companies that do not develop strategies will not be able to respond in a timely manner to the demands demanded by the current market.
According to García Paredes & Coronado Espinoza, a study where a sample of 367 Peruvian MSEs was surveyed, with the aim of knowing the level of application of strategic planning in them, it was concluded that "The situation found reveals a scarce formal use of strategic planning by the MYPES in the field of study associated with the little business culture coexisting with a low level of competitiveness in business".(6)
At the local level, there are numerous MYPES throughout the province of Cañete, according to MTPE (7), there are 37 167 MYPES that make up the list of accredited companies from January to December for the year 2017 in the National Registry of Micro and Small Enterprises REMYPE, of these 188 MYPES located within the 16 districts of the province of Cañete are identified.
Unfortunately, it is recognized that, in many of these micro and small companies, their representatives do not take advantage of the benefits of strategic planning and all that this implies, such as knowing in what situation the company is today and where it would like to go in the future, how it will achieve it, who will accompany it in the process, what are the risks and/or opportunities of the environment, what values will be present and put into practice, and many more. In these cases, the people who run an MSE usually carry out a planning that is largely an intuitive and less often formal planning, which complicates the fact that they can present themselves as a serious company.
In that sense, Quispe Chuchon(8) in his thesis, Proposal for Improvement in Strategic Management for the Quality Management of Micro and Small Enterprises in the Commerce Sector, Grocery Sector, Case: "Bodega Sueng", Cañete – 2019.
Despite the existing competition in the commercial sector, the owners or representatives of the company work empirically and since they contribute a lot to the country's economy, it should be considered that the MSEs work based on management strategies, with mission, vision, values, and strategies to increase their competitiveness.
In the place chosen for the research, Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C, it has been seen that there is a lack of shared strategic planning, and when the corporate mission and vision are not well defined, employees lack a guide that guides their performance to the achievement of organizational objectives, generating a weak organizational culture that affects the development of the company.
Among the different causes that may be causing this problem, the following have been detected: low valuation of the formulation of strategies, family influence in management, lack of time on the part of managers, low presence of leadership, limited use of technologies, low team participation, little considered human capital, presence of changing situations in the environment, poor situational diagnosis, lack of control of results, among others.
Strategy is indispensable in the organization because it represents a set of decisions that lead to action, without it is useless to have vision, mission, and objectives. For this reason, the strategy develops thinking about future situations and planning to achieve those situations.(9)
The effects that this problem can bring are many, among those detected are: loss of opportunities, lack of direction, disorganization, improvised actions, inadequate allocation of resources, dispersion of efforts, poor organizational communication, conflicts between the parties, environment of uncertainty, weak organizational culture, lack of motivation, low work performance, inefficiency, failure to meet goals, competitive disadvantage, loss of positioning in the market, Lower revenues, low profitability, loss of customers, stagnation and failure.
In order not to experience these terrible effects, it is important that the company defines and applies strategic planning so that the mission, vision and objectives, among other aspects, are clear; But not only by the managers of the company but by all those who make it up, contributing to form an organizational culture that can be put into practice by human resources, the main resource of any organization.
Gómez Zuluaga mentioned that "Being the organizational culture through the development of knowledge, human resources, quality, among other variables, those that sustain performance in the organization" (p. 172).(10)
Therefore, this research sought to determine how strategic planning is associated with the organizational culture of the bodega y viñedos Santa María in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021 and through it serve as a source of consultation by other companies and / or institutions, so that they apply strategic planning, Directing your organization to a long-term development with sustainability over time, grounding the dreams and ideas of an uncertain future to a concrete plan with strategies that allow obtaining results that benefit everyone: owners, shareholders, collaborators, customers and society.
The research work raised as a General Problem: How is strategic planning associated with the organizational culture of the bodega y viñedos Santa María of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021? , such as Specific Problems: 1) How is strategic planning associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021? , 2) How is strategic planning associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021? , 3) How is strategic planning associated with the adaptability of the bodega y viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021? , and 4) How is strategic planning associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021?
The research work proposed as a General Objective: To determine how strategic planning is associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , as Specific Objectives: 1) Determine how strategic planning is associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , 2) Determine how strategic planning is associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C.in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , 3) Determine how strategic planning is associated with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C.in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , and 4) Determine how strategic planning is associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
The research work proposed as a Specific Hypothesis: Strategic planning is significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , as Specific Hypotheses: 1) The strategic planning is significantly associated with the involvement of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , 2) Strategic planning is significantly associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. , 3) Strategic planning is significantly associated with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021., and 4) Strategic planning is significantly associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Given the lack of strategic planning in the MSEs that fosters, among other things, a poor organizational culture, where the actions of the people are not congruent with the objectives to be achieved and entail as their ultimate goal the non-continuity of the company; The interest arises to know the current situation of the company and from there identify if the strategies in the planning stage have a positive impact on the improvement of the organizational culture, so that the micro and small company manages to meet the objectives set.
The present research arises from the need to study an MSE in the province of Cañete, to determine the association between the variables: strategic planning and organizational culture.
The research seeks to provide information that will be useful to the community because the results of the study will contribute to promote improvements in the company Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. so that it remains a successful MSE that not only promotes tourism and provides jobs, but also contributes to the national economic GDP.
From a theoretical point of view, the research is justified because the study is based on concepts and theories that support the results that will be obtained.
Likewise, the study can serve as a theoretical source for other studies of the same nature, and as a source of consultation by other companies and / or institutions.
On the other hand, from a methodological point of view, basic research was carried out, because it is the study of a problem, destined exclusively to the search for knowledge.
However, limits are established to the research, since the results obtained from the study apply to the company in question and cannot be generalizable to all existing organizations due to the complexity of factors that could affect the organizational culture present in different contexts.
Finally, the research is feasible, since the necessary resources are available to carry it out.
Background
Meza Ariza, Guatibonza Tamayo,(11) in their scientific article, they point out that, the companies that make up the various sectors of the Colombian economy are currently affected by the constant changes in the business landscape, due to the instability and speed of changes in the market and demand, the client makes organizations more prepared and prepared to face changes that focus on aligning their organizational strategies to ensure their survival in the market, And this needs to see the development of an organizational culture that supports strategic planning to direct your efforts to achieve corporate goals. For the above reasons, this paper proposes a model in which organizational culture supports the implementation of strategic planning to ensure that business objectives are achieved.
Cuenca Galarza, López Paredes,(12) in their scientific article, they comment that the objective of the study was to analyze the organizational culture and commitment of FLACSO employees, using the questionnaire as a research tool based on the variables of interest, through the correlation technique, with evidence of the potential paths that talent experts must follow to model the culture of the organization.
Palafox Soto et al.(13) in their scientific article, they state that the study of organizational culture is becoming increasingly relevant in the current context, due to its importance as an intangible asset of the organization, that is why this article aims to identify the factors. elements of organizational culture through a systematic review, which contributes to the normal and lasting functioning of organizations over time. The main findings confirm that happiness at work, mission, vision, values, goals, leadership, participation and other factors affect the sustainability of the company. Therefore, organizations should give importance to the aspects that shape their culture, and that help companies survive over time, as well as continue to carry out literature reviews of this type as an important baseline for future research.
Ayres Farina et al.(14) in their scientific article, argue that, according to the Positive Psychology of Organizations and Work, flow and engagement are associated with the prosperity and success of a company. This study examines the relationship between flow and engagement, and introduces basic concepts about them. To this end, a literature review was carried out. Data collection is based on searching for products with the descriptive words "flow," "engagement," "personal resources," "business resources," and related terms. This search resulted in 49 studies that were read and categorized by information on content, year of publication, definition, genre, and related concepts. Between outcomes, processes and participation are associated with superior outcomes in business operations, worker performance, and life satisfaction. Studies show a wide range of uses, but more research is still needed.
Olugbola,(15) in his scientific article, he mentioned that, from a behavioral point of view, this study analyzes the impact of young people on entrepreneurship by identifying opportunities, driving factors, the impact of resources and entrepreneurial skills. In addition, the study examines the impact of entrepreneurship training on preparing young people to start a business and the elements of their success. The hypothetical inference method was used, through structural equation models in a population sample of 490 students from the University of Sains Islam Malaysia. The results highlighted the positive impact of identifying opportunities, motivations and resources available to students in entrepreneurship and the important role that entrepreneurship education plays in all factors, including morale and business. Corporate training shows that young people can thrive because individuality is truly a social phenomenon. This study views the individual as someone who can change throughout their life and provides additional information for those interested in how entrepreneurship can affect new businesses.
Yanet Huallpa,(16) in her master's thesis, presents his research as follows, the present research work aimed to determine the relationship between strategic planning (PS) and organizational culture (OC) in teachers of the educational institution Santísimo Nombre de Jesús-San Borja, 2020. It has been framed in empirical modeling, quantitative approaches, baseline types and association levels hypothetical inference methods and non-experimental cross-sectional design. Population and sample of 60 milestones. Deliberate non-probability sampling was applied. For data collection, a questionnaire was applied to each of the research variables through the survey technique. For the strategic planning tool, 5 dimensions, 11 indicators and 25 elements are considered, and Cronbach's alpha coefficient is applied, in which the α value of 0,96 is specified; You don't need to go through the authentication process (it was used in another survey you went through). On the other hand, the organizational culture tool was considered as 4 trends, 12 indicators and 25 items, confirmed by expert judgment, specific reliability and obtaining a α value of 0,952. The conceptual framework is based on the theory of strategic planning of Eyzaguirre (2006) with its five phases: philosophical, analytical, programmatic, operational and quantitative and for the changing cultural organization Denison (1996) is considered with four dimensions: participation, coherence, adaptability and mission. According to the results, it is possible to determine the relationship between strategic planning and organizational culture among teachers of the educational institution SNJ-San Borja, 2020. Based on the results obtained (p = 0,00; Rho = 0,664), it is concluded that there is a moderate relationship between PE and CO; this means that because there is better PE, there will be better CO among teachers.
Ore et al.,(17) in their scientific article, mentioned that strategic planning is a very useful tool in business management. Currently, the process is affected by the opposite scenarios that are being performed. The general objective of this study is to consider strategic planning as a management tool in companies and their profitability. Document searches are carried out in the database "Science Direct" and "Scielo" and in the manner described. The results show that strategic planning is a management tool in companies. It supports sound decision-making and acts as a structured guide with strategies for coping with future situations. You must take into account the four dimensions of analysis: planning, organization, direction and control. In addition, it has been determined that the strategic approach is linked to profitability, which is based on the relationship between net profit for the year and the investment made or net worth. No data were collected on the pilot study, leaving room for research to determine the impact of strategic planning on a company's profitability.
Llontop Herrera,(18) in his research work for high school, he carried out with the aim of knowing the importance of strategic planning in small and micro enterprises in Peru. To carry out the research, the descriptive analysis of the literature is used, taking references from previous research such as theses, academic articles and theories of books on the subject, from these sources the researcher finds that in Peru small and medium enterprises represent 95 % of all companies, so they are the ones that mobilize and energize the economy of the country, 50 % of them died before the first year of operation. Surveys of the indicated number have been created to determine why MSEs are not kept in the market, and from these investigations it can be determined that some of the most important factors are those classified as managerial, strategic and personal, related to limited managerial capacity. of the owners of this type of business, the lack of planning within the company and the lack of capacity for the management of the company's resources. Therefore, we conclude that using the concepts and tools provided by strategic planning, it is possible to solve the strategic, managerial and personal problems faced by MSEs, to support their continuity and development in the market.
Ataucusi Catay,(19) in his undergraduate thesis, he shows his research as follows, the main objective of this study is to determine the impact of strategic planning on the business management of the Mega Centro 1 040 shopping center in 2018. The study uses the scientific method, the type of applied research and degree of association, non-experimental design - treatment - correlation. The community of 75 microentrepreneurs of the shopping center was studied and a census sample was applied. The technique used is the survey using its own tool, the questionnaire. For the construction of the instrument, a Likert-type scale was used, composed of 24 items depending on the size of the variables. The results on aspects of the strategic planning variable show that more than 78 % of small entrepreneurs do not know the strategic philosophy of the shopping center. Regarding external and internal audits, only 4 % of small entrepreneurs said they strongly agreed with the effectiveness of management. In terms of strategy formulation and selection, only 8 % of small business owners said they agreed that the strategies they adopt ultimately work. Similarly, the results against the dimensions of the business management variable show that more than 90 % agree that corrective actions should be taken to improve current management practices. The study concluded that strategic planning has a positive and significant impact on business management (Spearman's Rho 0,623), which means that if a strategic plan is implemented, the commercial management of shopping centers will be improved.
Silva Borja,(20) in his doctoral thesis, he details that, without a doubt, strategic planning is fundamental for a better organization, who without it would have great administrative difficulties, and find the UNACH Admissions and Promotions unit overwhelmed with this same new unit, whose internal organization is unknown. To solve this problem, the following work entitled "Strategic Planning and Administrative Management of the Settlement and Registration Unit, National University of Chimborazo, city of Riobamba - Ecuador" is presented, this study focuses on the preliminary discovery of the origins of development. From the current epistemology of the subject that the administrative management and the process of planning, direction, regulation and control of its development is based on the development of a new educational unit that focuses on its needs. In developing our research, we use discovery techniques to identify unit problems. Similarly, quantitative evaluation is applied to determine the percentage characteristics of the research subjects through surveys and observation sheets with 4 authorities, 4 administrative and 40 teachers. After obtaining the pertinent information, the analysis and interpretation of results was carried out, through the frequency tables and graphs in which it was obtained that there is a significant relationship between strategic planning and administrative management with 0,876 being a level of significance of very good relationship.
Carranza Lagos et al.(21) in his master's thesis, he states that the market for alcoholic beverages in Peru and especially in Lima is constantly growing, but compared to the region consumption is still low. If we only measure the consumption of spirits, we have Pisco as the beverage with the highest growth and participation in this category. Pisco as a national drink is fully supported by the state, based on the determination of the origin of Peruvian pisco, as well as laws that protect and encourage the consumption of real pisco in Peru. There are different pisco brands on the market of all kinds, some focus on price and others focus on the characteristics that only a good pisco usually has. On the other hand, consumers in Peru learn to consume this spirit very slowly and know very little about it. The internal and external evaluation of the pisco market shows a great opportunity for growth in the consumption of this drink, as well as a growing segment of people over 18 years old and under 40 years old with lifestyles that can help increase the knowledge and consumption of Peruvian pisco. The proposal is to provide an alternative to the consumption of pisco in Peru, which will be different from those that already exist in the Peruvian market, aiming at the sector with the greatest participation, which have the desire to produce and consume differently from other products. This different variant called Jolly Roger, promoted by La Bodega Santa María, offers us the best selection of youth, difference and quality that this great field seeks.
Díaz Inca,(22) in his master's thesis, he presents his research as follows, the general objective of the thesis is to explain how strategic planning affects the financial management of the Mypes business in the capital Lima, period 2015-2016. The methods used are quantitative, causal and longitudinal, non-experimental design and the survey applied as a measurement tool. Finally, according to the R2 test, a causal relationship of 0,877 was determined, which is equivalent to 87,7 % that the financial management of the dependent variable has a causal effect on the strategic planning variable.
Alarcón Aburto,(23) in his undergraduate thesis, he points out that strategic planning is a systematic process of applying tools that allow a company to grow to achieve its goals and objectives for business success. The study aimed to determine the influence of strategic planning on the commercial development of MSEs in Ciudad de Dios - SJM, 2018. Study of the quantitative approach, type of application, explanatory or causal cross-sectional level, non-experimental design. The village has 60 Mypes. Two scales are used: Strategic Planning and Business Development, which consists of 20 questions for both tools, confirmed by tests of expertise and reliability using Cronbach's Alpha, respecting ethical considerations. The results obtained in a strategic plan greatly affect the commercial development of the City of God. Regarding size: the organizational task, vision and organizational objectives of the organization with business development, it has been found to have a great impact. In conclusion, there is an influence between the two variables. Thus, strategic planning in MSEs establishes unified operations as planned in management. Based on the identification of problems and defects that prevent the continuous improvement of the company. In addition to guaranteeing the quality of the service and the good development of the company. Implementing strategic planning helps prevent planning from failing, minimizes risks, and increases productivity and performance.
Goicochea Centeno,(24) in his undergraduate thesis, he exposes his research as follows, in the district of Imperial province of Cañete, there are many restaurants that operate in the market, but many of these do not know and do not have enough information about Quality Management processes and how important it is to apply strategic planning for your company. To address this issue, the following general objective has been proposed: Elaboration of a proposal to improve the strategic planning of quality management for small and micro service companies, catering, state: La Isla Del Sabor, Imperial - Cañete, 2019. The study was quantitative - descriptive, and survey techniques and questionnaire tools were used. The following results are obtained. 100 % of representatives said the restaurant did not have a strategic plan, 100 % of representatives said the restaurant had no formal organizational structure, and 100 % of representatives said the restaurant was popular with diners. It can be concluded that strategic planning is important for MSE, knowing the principles of quality management will help MSE to be more responsible with quality and ethics in general.
Theoretical bases
Strategic Planning Variable
Management by objectives
By the 1950s, management directed the focal point toward the goals and ends of the organization. The focus on results brought a change in management knowledge, where work ceased to be an end and became a means to obtain results. Thus, management by objectives (APO), or by results, emerged in 1954, with Peter F. Drucker, considered the father of management by objectives.(25)
Harold Koontz, (1994), in his definition of Management by Objectives (A.P.O.) presents it as "a complete administrative system that integrates many fundamental administrative activities in a systematic way consciously directed towards the effective and efficient achievement of organized and individual objectives"(26)
Works in a democratic and participatory manner, laying the foundations to evaluate human performance and above all to reconcile the objectives of the organization with the individual. In that sense, the APO works according to the following scheme:
· The manager and subordinate meet, discuss, negotiate, and together formulate the objectives of the subordinate's performance. Together they negotiate objectives, goals, and outcomes. The objectives are formulated in a consensual and participatory way.
· From that point on, the manager is committed to providing the support, direction, and resources necessary for the subordinate to work effectively to achieve the goals. The manager demands results and guarantees the means and resources (training, skills, equipment, etc.) so that the subordinate can achieve them.
· The subordinate sets to work to achieve the goals and demands the necessary resources to achieve the objectives.(25)
Management by objectives (APO) and management focused on results, are two current and practical methods, typical of modern management, which have been characterized as great allies of the achievements and fulfillment of the objectives that have been raised by the organization.(27)
Phases for the Development of Strategic Planning
According to Chiavenato,(28) strategic planning "refers to the way in which a company tries to apply a certain strategy to achieve the proposed objectives. It's generally global, long-term planning." To this end, it proposes the following phases:
· Formulation of organizational objectives: the company chooses the global objectives that it intends to achieve in the long term and defines the order of importance and priority of each one in a hierarchy of objectives.
· Internal analysis of the company: this is an organizational analysis; that is, a study of internal conditions, to allow an evaluation of the main strengths and weaknesses existing in the company. Strengths constitute the propelling strengths of the enterprise that facilitate the achievement of organizational objectives, while weak parts constitute the constraints and restrictive forces that hinder or impede the achievement of those objectives. In the internal analysis includes the analysis of resources, analysis of the organizational structure of the company and the evaluation of performance based on results.
· External analysis of the environment: this is an analysis of the external environment; that is, the external conditions that surround the company and that impose challenges and opportunities. Such an analysis covers the markets served by the company, competition, and external factors.
· Formulation of strategic alternatives: it seeks to formulate the various and possible strategic alternatives or means that the company can adopt to better achieve the proposed organizational objectives, taking into account its internal conditions and the external conditions existing around it. Strategic alternatives are the future courses of action that the company can adopt to achieve its overall objectives.(26)
Conceptual Model of Development and Implementation
On the other hand, Steiner (1996) contributes to strategic planning, considering the following model:
· Situation analysis: Its purpose is to identify and analyze the key trends, forces and phenomena that have a potential impact on the formulation and implementation of strategies. Includes:
· Expectations of external elements: These are those individuals and groups with such an important interest in the company's business that their views should be taken into account in the strategic planning process.
· Expectations of people within the company: The interests of both managers and workers are changing, and companies are taking them into account in their planning process, since when they manifest themselves in a powerful way, they represent basic premises for planning.
· Analysis of data about past performance: They are useful as a basis for assessing the current situation and possible future development.
· Analysis of data about the current situation: The volume of information about the current situation is much greater than that referring to past performance. It should include analysis of clientele and market, company resources, competition, environment and other performance measures or areas of interest.
· Forecasting: Refers to the possible future results and performances of the organization and the influence of the environment on it.
· Identification of opportunities, hazards, potentialities, and weaknesses: It must result in an accurate list of weaknesses, opportunities, dangers, and potentialities. This information is very useful when reviewing missions and purposes, when setting long-term goal attempts, and when devising program strategies.
· Formulation of missions and objectives: One of the most important responsibilities of senior management is to formulate the purposes and missions of the organization. Only based on purposes and missions can more detailed objectives, strategies and tactical plans be developed. The planning process requires that the general premises of missions and purposes be made more concretely through the development of long-term objectives. After performing this step, it is possible to plan specific strategies to achieve the objectives and purposes.
· Development of strategies and policies: Once the purposes and missions and the basic objectives of long-term planning have been established, the conceptual sequence in strategic planning is to develop the program of strategies to achieve it.
· Development of programs with strategic course: Refers to the acquisition, use and disposition of resources for specific projects. The identification of the main strategies should lead to the identification and subsequent evaluation of sub-strategies. All strategies must be divided into sub strategies to achieve a successful implementation. Successful strategies are, in reality, a group of interrelated strategies.
· Preparation of short-term plans and budgets: This part of planning is very significant, since it establishes the credibility of strategic plans and provides the basis for their effective implementation.(26)
Strategic Planning Schools
"The process of strategic planning has varied over the years, where two schools are evident: one of a fixed perceptual and normative nature, and the other of a descriptive and explanatory nature."(25)
In total, the ten schools of strategic management that systematize Mintzberg, et al. (1998).
Perceptual and normative schools:
· Planning school: Strategy formulation is approached as a formal process in which operational plans are broken down. Breakdown of strategic objectives into tactical and operational objectives. "Ansoff (1965), introduced the school of strategic planning management. In addition, Steiner offers an integrated model of strategic planning according to this school's approach."
· School of design: strategy is approached as a process of adequacy. The formulation of strategies serves to regulate the internal factors of the organization with the external factors. "In 1957 Selznick introduced the so-called design school of strategic management (SWOT)."
· School of positioning: strategy is approached as an analytical process. Strategic planning seeks to position the organization in the external environment against the competition. "The strategic positioning management school was introduced in the mid-70s by Schendel & Hofer (1979), based on disciplines such as military history, industrial organization and economics."
Descriptive and explanatory schools:
· School of entrepreneurial initiatives: the strategic plan is developed based on the vision that the leader of the organization has about the prosperity of the company. "The business school was introduced by Schumpeter. This strategy centralizes power in a charismatic, positive and at the same time bold leader to intuitively decide the actions necessary to lead or improve the company (Schumpeter, 1934)".
· Cognitive school: strategy is approached as a mental process. The way in which people perceive and interpret the reality of the environment is taken into consideration. "Simon (1947), introduced the cognitive school with a statement of intent: "I will see it when I believe it." It interprets reality according to the maps of solutions and interpersonal schemes that solve the problems."
· School of learning: strategy is understood as an emergent process, that is, strategies are formulated while a process of learning and reflection of past situations takes place. "The school of strategic learning management that Lindblom inaugurated (1959), is inspired by psychology, education and mathematics. It proposes to learn new tools to make sense of the company's work."
· School of power: Strategy is a process of negotiation. Strategic planning consists of the negotiation of strategies for the dispute of power. "Allison (1971), unveiled the school of strategic management of power, according to principles of political science and negotiation."
· School of culture: addresses strategy as a collective and social process. Strategic planning is based on organizational culture. "The school of cultural strategic management was introduced by Rhenman and Normann in the late 60s in Sweden... This management rescues the values, convictions and myths that unite and give meaning to an organizational situation."
· School of the environment: strategy is approached as a process that reacts to external circumstances. The organization is understood as a passive factor in the face of the environment. "For its part, the school of strategic environmental management released by Hannan & Freeman (1977), point out that in human relations "everything depends" on the environment in which organizations operate and the adaptability of their components.
· School of configuration: approaches strategy as a process of transformation. Strategic planning consists of reconfiguring strategies based on changes in the environment. "Finally, Chandler (1962), presented the school of strategic management called configuration, which proposes to group forces to revolutionize structures."(29)
Organizational culture variable
Human Relations Theory
The theory of Human Relations (or Humanistic School of Management) emerged in the United States, because of the conclusions of the Hawthorne experiment and was later developed by Elton Mayo and his collaborators.
The emergence of the theory of Human Relations brought a new language that would dominate in administrative language; This theory talks about motivation, leadership, communication, informal organization, group dynamics, etc. In addition, it harshly questions or sets aside the classic concepts of authority, hierarchy, rationalization of work, departmentalization, general principles of Administration, among others. Suddenly, the other side of the coin begins to be explored: the engineer and the technician give their place to the psychologist and the sociologist. The method and the machine lose their primacy in the face of group dynamics; Human happiness is conceived from other points of view, because homo economicus is replaced by social man. This evolution in the discipline, which emphasized its democratic character, occurred at the dawn of World War II. The importance given to tasks and structure was concentrated on people.(25)
Edgar H. Schein's Organizational Culture and Leadership Proposal
Schein's work has been considered the most considerable effort to integrate studies about organizational culture and is one of the most celebrated proposed for its easy understanding and practical application in organizational environments.
The theoretical starting point for Schein's work is that organizations – like biological organisms – must successfully perform several functions to survive, the basic theoretical assumption being that organizational survival is the key to the understanding of organizations. The main argument is that, to survive, any organization must solve two fundamental problems: (i) survival in and adaptation with the external environment and (ii) integration of its internal processes to ensure the ability to continue surviving and adapting.
In that framework, he defines organizational culture as "a pattern of basic assumptions – invented, discovered, or developed by a group as it learns to handle its problems of external adaptation and internal integration – that has worked well enough to be considered valid and, consequently, taught to new members as the correct way to perceive, think and feel in relation to those problems."
This interesting and complex definition indicates that culture involves assumptions, adaptations, perceptions, and learning. The first three concepts are found in the elements and levels in which culture operates, and the fourth in a behavioral, cognitive, and emotional process developed through the mechanisms of affirmation, expression, and transmission of culture. On the other hand, the concepts of external adaptation and internal integration are generally associated with the functions of the organizational culture.(30)
Daniel R. Denison's Organizational Culture Model
The model developed by Denison is based on a correlation between organizational culture and frontline performance measures (return on investment, sales growth, quality, innovation, employee satisfaction). It was developed from a series of studies that examined the impact of organizational culture on performance and led to the identification of four impacting characteristics: engagement, consistency, adaptability, and mission. The central idea put forward by Denison is the "strong culture hypothesis," which holds that, to achieve significant performance gains, culture needs to be both strong and distinctive.
The model recognizes that cultural characteristics, managerial behaviors, and even organizational strategies can be linked to a set of beliefs and assumptions about the organization and its environment. These core beliefs and assumptions lie at the heart of an organizational culture.
The model then offers four types of culture:
· Culture of adaptability: characterized by a strategic concentration on the external environment through flexibility and change to meet the needs of consumers.
· Mission culture: Places crucial importance on a shared vision of organizational purpose.
· Culture of involvement has a main concentration on the involvement and participation of the members of the organization.
· Culture of consistency has an internal concentration and gives an emphasis to the stable, methodological, and cooperative proposal of doing business.
The way Denison approaches culture is eminently operational and defined by and towards performance based on organizational efficiency.(30)
Dimensions of strategic planning
Regarding the first variable, strategic planning, it was taken into account among other approaches; to the Management by objectives (APO) of Peter Drucker, the phases of strategic planning proposed by Idalberto Chiavenato and the conceptual model of development and implementation of Steiner, considered when structuring the proposed dimensions:
· Strategic analysis. "Its purpose is to identify and analyze key trends, forces and phenomena that have a potential impact on strategy formulation and implementation." Naranjo Pérez et al.(26)
· Strategic direction. It consists of raising those elements such as: Mission, Vision, Objectives and Values; that the company intends to achieve and that will be the basis on which all its actions and behaviors will be directed.
· Strategic formulation. "It seeks to formulate the various and possible strategic alternatives or means that the company can adopt to better achieve the proposed organizational objectives, taking into account its internal conditions and the external conditions existing around it."(26)
Dimensions of organizational culture
The present research, regarding the second variable, organizational culture, was based on the Theory of Human Relations, the proposal of organizational culture and was used as the main approach; the Denison Organizational Culture Survey designed by Daniel Denison of the University of Michigan.
The questionnaire was developed to measure culture in organizations and can be applied in multiple contexts. It consists of 60 questions in total, 5 questions for each of the 12 subdimensions, grouped into 4 dimensions:
· Implication. "It refers to the power of its members who are organized in teams, the sense of commitment and belonging of the members with their work and organization, which leads them to be participants in decisions related to the objectives of the company."
· Consistency. "The activities are properly coordinated. What characterizes organizations with consistency, is the stability and integration they show, as a result of a shared vision and a high degree of uniformity."
· Adaptability. "The ability of the organization to adapt and introduce changes, which generally result in sales growth and favor the increase of market shares."
· Mission. "It represents purpose over goals and strategic objectives outlined, providing a clearer vision of the organization going forward." Contreras Cueva & Gómez Gómez(31)
METHODOLOGY
Fernandez Collado & Baptista Lucio mentioned that "Research is a set of systematic, critical and empirical processes that are applied to the study of a phenomenon or problem."(32)
Research method
Godoy mentioned that "The method is the way forward through a series of operations, rules and procedures fixed in advance in a voluntary and reflective way, to reach a certain end, which can be material or conceptual".(33)
In turn, it should also be noted that:
The way of knowing and proceeding that science must be called, according to Ezequiel Ander-Egg, scientific method. This method has certain characteristics that are essential and interrelated: 1) it is factual, that is, the facts are its source of information and response; 2) transcends facts: it is about knowing, understanding and explaining the facts, not describing them; (3) adheres to methodological rules, i.e. pre-established operations and procedures; 4) verifies empirically, to formulate answers to the problems raised and to support its own claims; 5) due to the permanent confrontation it is a self-correcting and progressive method; 6) its formulations are of a general nature; 7) is objective insofar as it seeks to attain factual truth.(33)
In this way we can say that "The scientific method is a series of orderly, systematic, reflective and critical steps that are used to obtain scientific knowledge."(34)
The present research used the scientific method as a general method; since the phases of observation, proposal of the hypothesis and issuance of conclusions were developed; and the statistical method, as a specific method; Because the thesis focused on the calculation of sampling and interpretation of the data collected.
Research approach
We can understand as an approach that perspective under which the research was approached in terms of data collection for the study of reality. "For Blaxter, Hughes and Tight (2000), approaches are what some call the methods or simply the techniques of data collection.(35)
When planning an investigation, it is important to establish in advance what kind of data will be obtained, whether they are quantitative or qualitative. Cid et al.(36)
In that sense, Niño Rojas (35) noted "a characterization of quantitative and qualitative research. Apparently opposed (one measures, the other understands), their borders are not easy to delimit. And in practice they complement each other."
Since we sought to test the previously established hypothesis and measure the variables, making use of non-probabilistic statistics, to collect and analyze information obtained from strategic planning and organizational culture surveys, with 28 and 60 questions respectively, the present work was elaborated under the methodological approach of the quantitative approach.
According to García Manjón,(37) this approach "As the word implies, quantitative research is concerned with 'quantity' and therefore its primary means is measurement and calculation."
Regarding the quantitative approach, the University for International Cooperation said that "This approach uses logic or deductive reasoning, which begins with theory and from these logical expressions called hypotheses are derived that the researcher seeks to test."
Type of investigation
A typology of the types of research refers first to two large sections: pure research and applied research. Baena Paz(9)
According to the purpose pursued, the type of research is pure or basic, because it was the study of a problem, intended exclusively for the search for knowledge.
In this regard, Baena Paz,(9) indicated that:
The pure sciences are those that propose to know the general laws of the phenomena studied, elaborating theories of wide scope to understand them, and that ignore – at least immediately – the possible practical applications that can be given to the results.
Research design
Fernandez Collado & Baptista Lucio mentioned that "The researcher must visualize the practical and concrete way to answer the research questions, in addition to meeting the objectives set. This involves selecting or developing one or more research designs and applying them to the context of your study.(32)
In fact, Fernandez Collado & Baptista Lucio(32) mentioned Design in terms of research as the "Plan or strategy that is developed to obtain the information that is required in an investigation and respond to the approach."
Because there was a group or representative sample to which an instrument was applied to obtain answers that lead us to results without the need to produce a change in those investigated, it can be established that the research applied a descriptive design.
From the descriptive research Niño Rojas,(35) he said that Its purpose is to describe the reality under study, an aspect of it, its parts, its classes, its categories, or the relationships that can be established between several objects, to clarify a truth, corroborate a statement or verify a hypothesis. It is understood as the act of representing by means of words the characteristics of phenomena, facts, situations, things, people, and other living beings, in such a way that whoever reads or interprets, evokes them in the mind.
In conclusion, the research work corresponds to the Non-experimental Research Design, because the variables strategic planning and organizational culture were observed in their natural context, and then analyzed without manipulating the variables in order to see their effect; of cross-sectional cut, since the data are given in a single moment, year 2021 and descriptive, because the reality was described to corroborate the hypothesis, strategic planning is significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Level of research
The level of research refers to the degree of depth and scope that is intended with it. The research is of correlational level since "It has the purpose of measuring the degree of relationship that exists between 2 to more concepts or variables". and the behaviors of the variables are described to establish incidence relationships. To this end, the present research work measured the degree of association between the strategic planning variable and the organizational culture variable.(38)
Population
The population of this research was made up of the administrators and collaborators of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the Lunahuaná district of the province of Cañete in the period 2021.
|
Table 1. Study population |
|
|
Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. |
|
|
Administrative |
03 |
|
Collaborators |
07 |
|
Total |
10 |
Sample
In this regard, in the present study, the sample must be non-probabilistic census, where:
· The Administrative. - Made up of senior management staff, it comprises a total population of 03 people, of which the entire population must be considered as a sample.
· The Collaborators. - Made up of operational personnel, it comprises a total population of 07 people, of which the entire population must be considered as a sample.
· Therefore, in the present research the sample was equal to the size of the population because it is a small universe, so we worked with 100 % of the population.
Techniques, instruments, and data processing
Data collection method
The main data collection method used in the research was non-probability sampling.
Data collection technique
The main data collection technique used in the research was the survey, through a set of questions addressed to the representative sample of the company, opinions and specific facts about the problem investigated were known.
Data collection instrument
The main instrument used in the research was the questionnaire.
Validation of the instrument
Expert judgment.
Reliability technique
Cronbach's alpha coefficient. Once the data was collected, they were tabulated, for their respective process and analysis.
Data processing and analysis
Data processing is the set of means that will be applied to convert data into information, by organizing the elements obtained during their collection. Data analysis consists of examining data by the meaning they represent in research.
Data Type: Quantitative Data
Type of Statistical Data Analysis: Descriptive
Tools: Descriptive statistics. frequency, percentages and graphs, normality tests.
Hypothesis Test: Nonparametric Tests (Rho Spearman).
Program: SPSS, as an explorer of data previously obtained by instruments subjected to reliability and validity tests. In this regard, Guisande Gonzalez et al. (39) point out that "The SPSS program allows the position and dispersion measurements to be calculated in a simple way".
The results have been analyzed statistically, to observe the contrast of the hypothesis, the same that are presented in tables, figures and others for their respective interpretation.
RESULTS
Strategic Planning Database
Regarding the strategic planning variable, a questionnaire with 28 questions was applied and the Likert scale was used for its qualification, with five answers at the following level:
· Never = 1
· Almost never = 2
· Sometimes = 3
· Almost always = 4
· Always = 5
· Database of the strategic planning variable
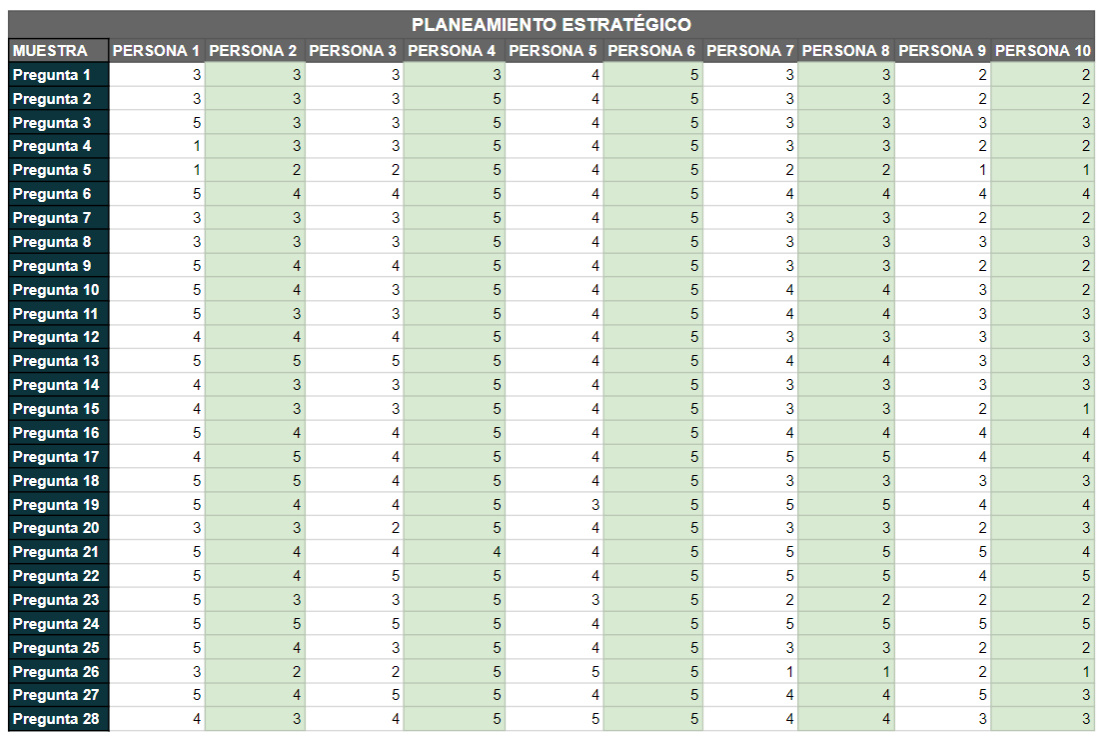
Figure 1. Database of the strategic planning variable
Organizational culture database
Regarding the organizational culture variable, a questionnaire with 60 questions was applied and the Likert scale was used for its qualification, with five answers at the following level:
· Strongly disagree = 1
· Disagree = 2
· Neutral = 3
· Agree = 4
· Strongly agree = 5
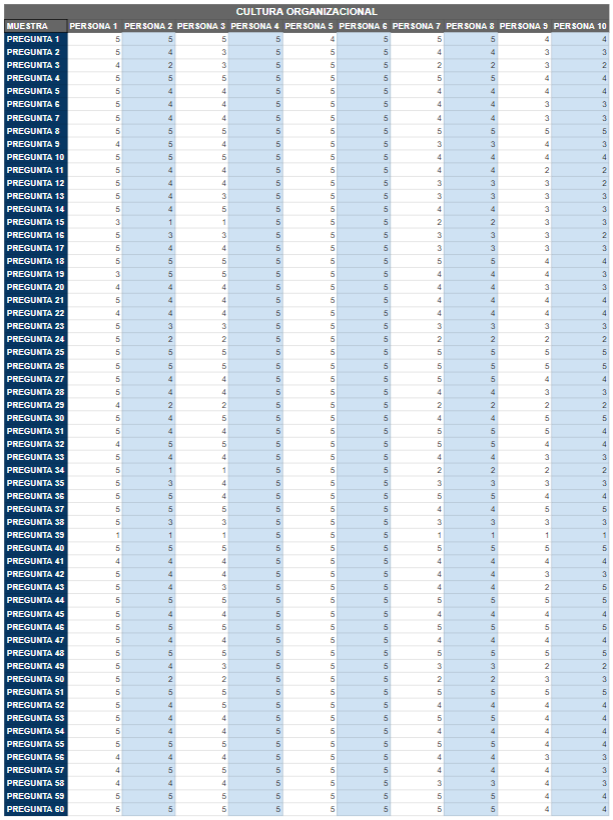
Figure 2. Database of the organizational culture variable
Analysis of the results
Descriptive statistics
Variable: Strategic planning
According to table N°2 and figure N°3, regarding the strategic planning variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, it is necessary that, of the total respondents, 30,0 % (n = 3) manifest a Regular Level, which indicates that the company carries out strategic planning, but it does not have it reflected in a plan and 70,0 % (n = 7) manifest a High Level, which indicates that the company carries out strategic planning, the same as reflected in a plan.
|
Table 2. Variable: Strategic planning |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
3 |
30,0 |
|
High |
7 |
70,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
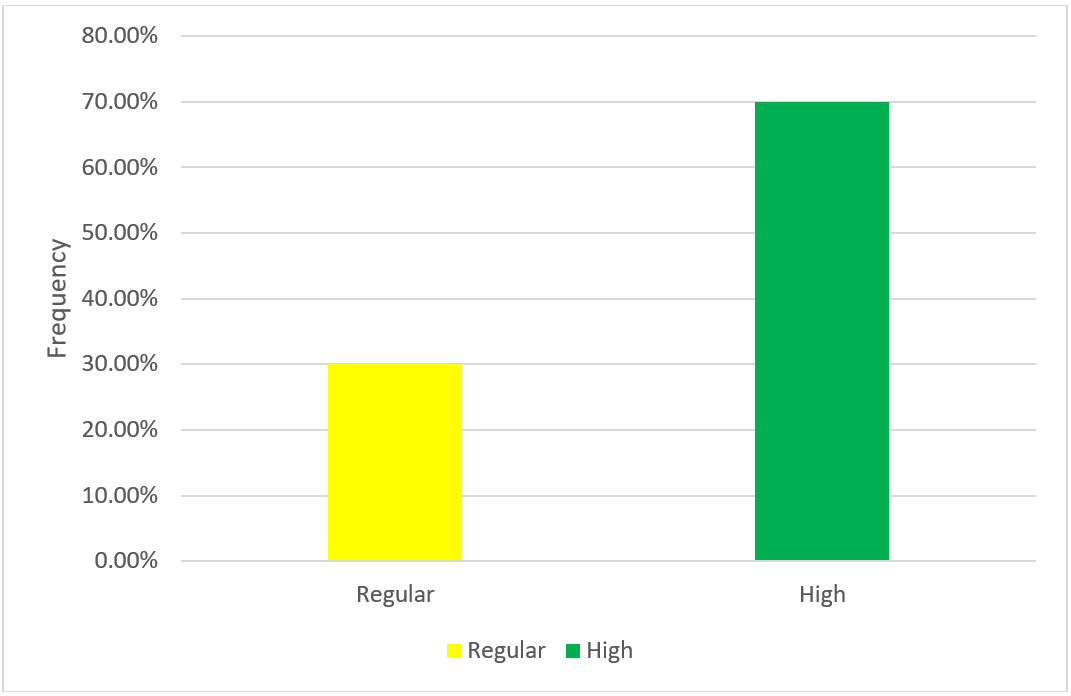
Figure 3. Variable: strategic planning
Dimension: Strategic Analysis
According to table N°3 and figure N°4, regarding the strategic analysis dimension of the strategic planning variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 20,0 % (n=2) manifest a low level, which indicates that the company does not perform strategic analysis; 50,0 % (n=5) manifest a regular level, This indicates that the company performs strategic analysis, but not continuously and 30,0 % (n = 3) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company performs strategic analysis continuously.
|
Table 3. Dimension: strategic analysis |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
2 |
20,0 |
|
Regular |
5 |
50,0 |
|
High |
3 |
30,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
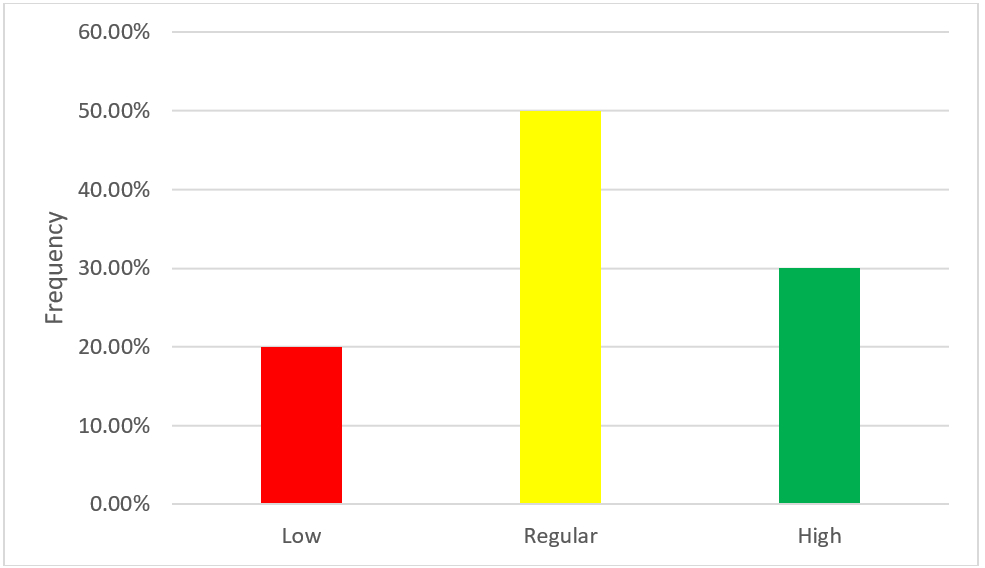
Figure 4. Variable: strategic analysis
Dimension: Strategic direction
According to table N°4 and figure N°5, regarding the strategic direction dimension of the strategic planning variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 30,0 % (n = 3) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has strategic direction, But it does not encourage it and 70,0 % (n=7) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has strategic direction and often encourages it.
|
Table 4. Dimension: strategic direction |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
3 |
30,0 |
|
High |
7 |
70,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
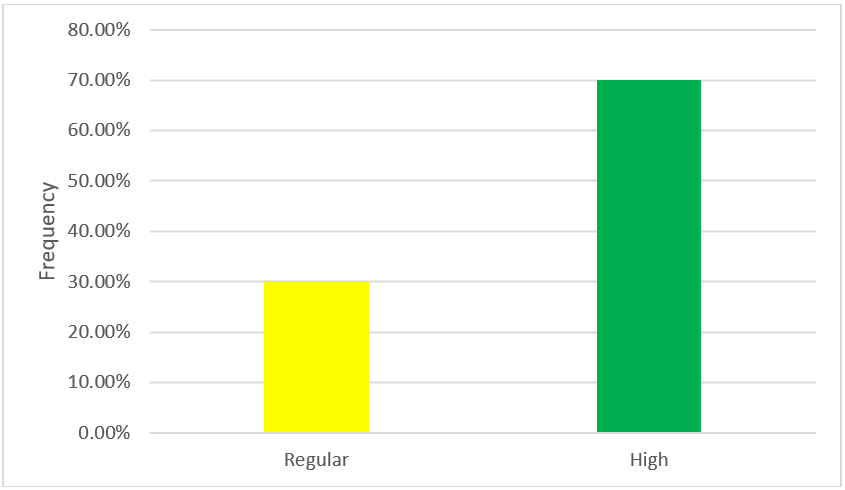
Figure 5. Dimension: strategic direction
Dimension: Strategic formulation
According to table N°5 and figure N°6, regarding the strategic formulation dimension of the strategic planning variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 40,0 % (n=4) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company carries out strategic formulation, but intuitively and 60,0 % (n = 6) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company formally makes strategic formulation.
|
Table 5. Dimension: strategic formulation |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
4 |
40,0 |
|
High |
6 |
60,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
Variable: Organizational culture
According to table N°6 and figure N°7, regarding the organizational culture variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 20,0 % (n=2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular organizational culture and 80,0 % (n=8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good organizational culture.
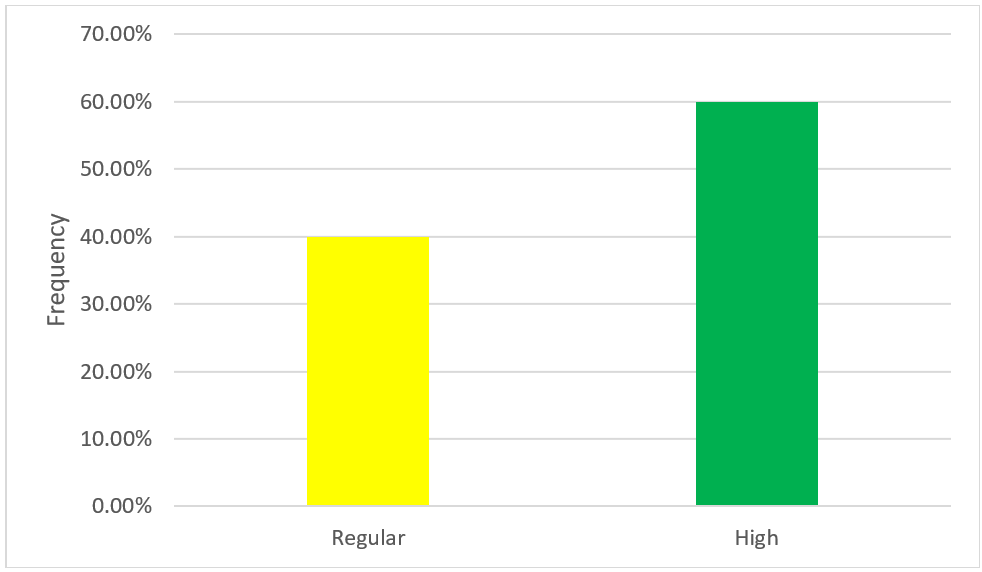
Figure 6. Dimension: strategic formulation
|
Table 6. Variable: organizational culture |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
2 |
20,0 |
|
High |
8 |
80,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
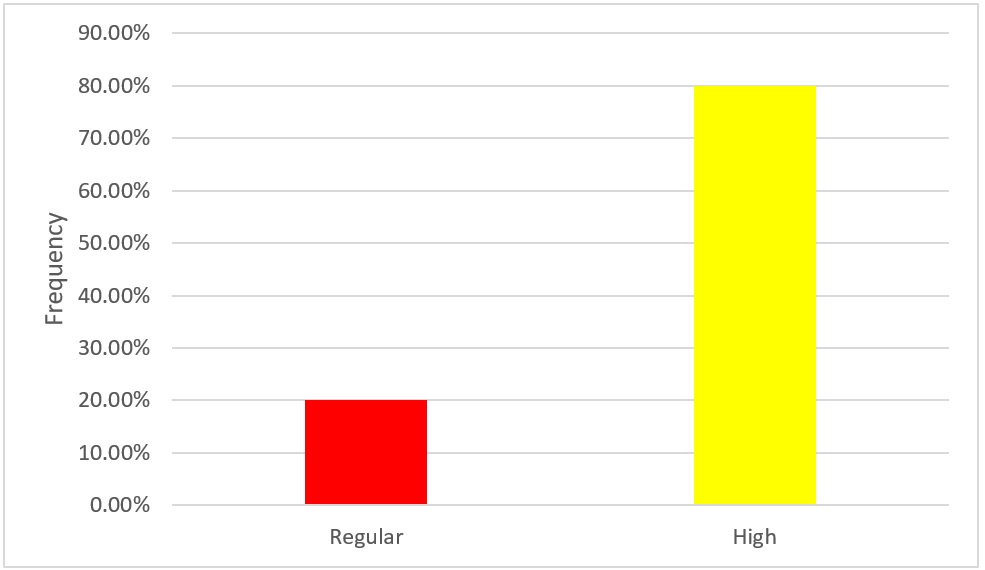
Figure 7. Variable: organizational culture
Dimension: Implication
According to table N°7 and figure N°8, regarding the dimension implication of the organizational culture variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 10,0 % (n=1) manifest a low level, which indicates that the company has a bad involvement; 10,0 % (n=1) manifest a regular level, This indicates that the company has a regular involvement and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good involvement.
|
Table 7. Dimension: involvement |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
1 |
10,0 |
|
Regular |
1 |
10,0 |
|
High |
8 |
80,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
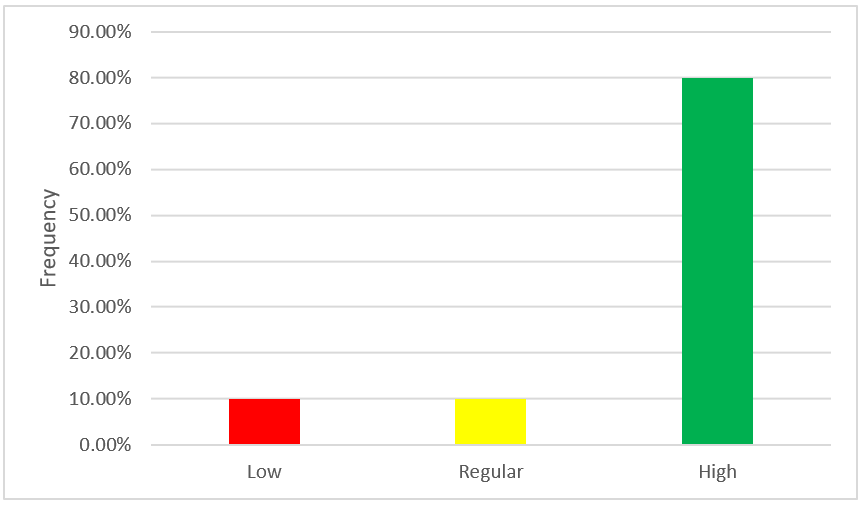
Figure 8. Dimension: involvement
Dimension: Consistency
According to table No. 8 and figure No. 9, regarding the dimension consistency of the organizational culture variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 20,0 % (n = 2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular consistency and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good consistency.
|
Table 8. Dimension: consistency |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
2 |
20,0 |
|
High |
8 |
80,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
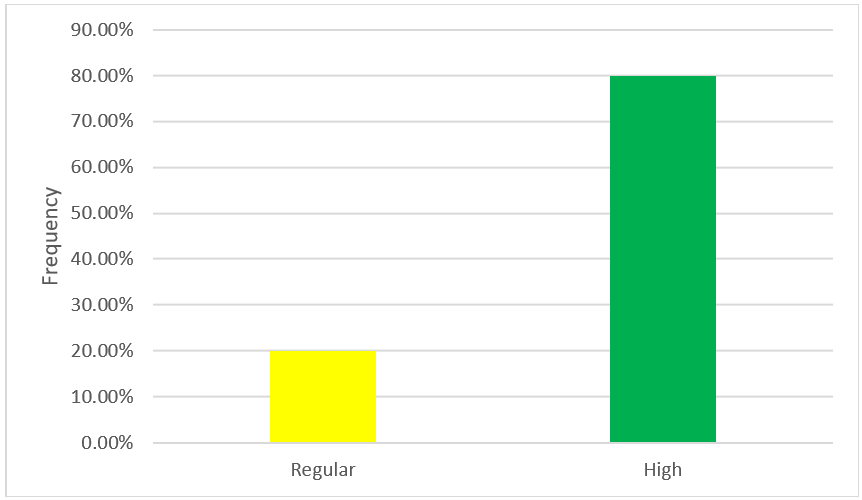
Figure 9. Dimension: consistency
Dimension: Adaptability
According to table N° 9 and figure N° 10, regarding the adaptability dimension of the organizational culture variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, 40,0 % (n=4) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular adaptability and 60,0 % (n= 6) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good adaptability.
|
Table 9. Dimension: adaptability |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
0 |
0,0 |
|
Regular |
4 |
40,0 |
|
High |
6 |
60,0 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
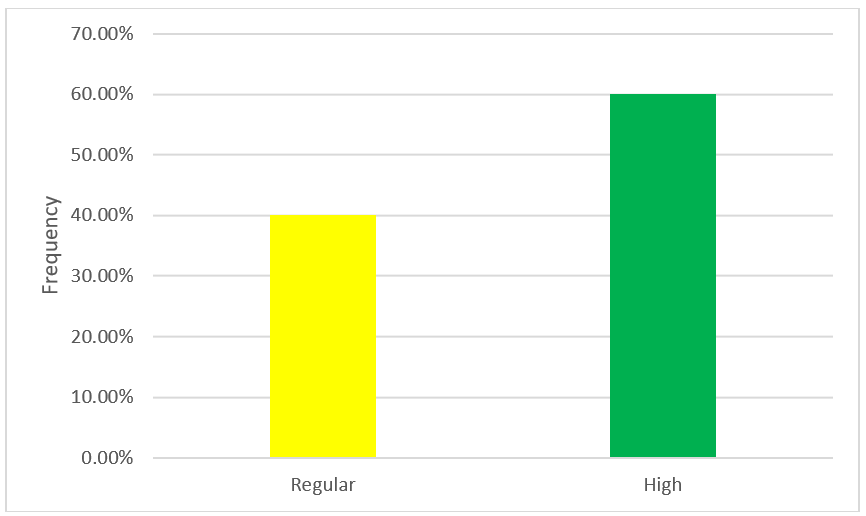
Figure 10. Dimension: adaptability
Dimension: Mission
According to table N° 10 and figure N° 11, regarding the mission dimension of the organizational culture variable of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, it is necessary that 10,0 % (n=1) manifest a low level, which indicates that the company has a bad mission; 20,0 % (n=2) manifest a regular level, This indicates that the company has a regular mission and 70,1 % (n=7) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good mission.
|
Table 10. Dimension: mission |
||
|
|
Frequency |
Percentage |
|
Low |
1 |
10,0 |
|
Regular |
2 |
20,0 |
|
High |
7 |
70,1 |
|
Total |
10 |
100,0 |
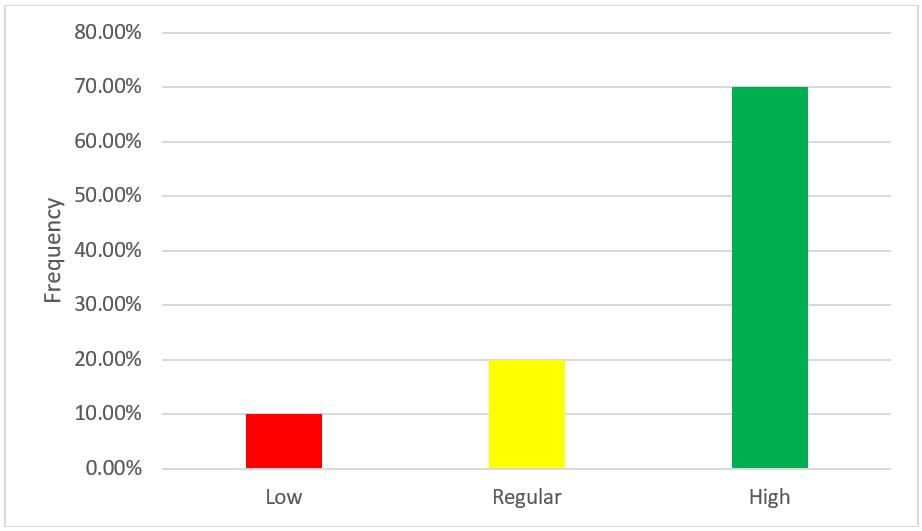
Figure 11. Dimension: mission
Evaluating the Hypothesis
Normality Tests
According to Table No. 11, the normality test was applied for the analysis of the data, using the statistical test of Shapiro Wilks, since there is a sample less than 50, from which the values of p_valor = 0,000 are verified for the strategic planning variable; p_valor = 0,000, for the organizational culture variable, p_valor = 0,000, for the Involvement dimension, p_valor = 0,000, for the consistency dimension, p_valor = 0,000, for the adaptability dimension, and p_valor = 0,000, for the mission dimension, so all values are less than 0,05, indicating that the data do not come from a normal distribution, so nonparametric statistics will be used to contrast the hypotheses.
|
Table 11. Normality tests |
|||
|
|
Shapiro - Wilks |
||
|
Statistical |
Gl |
Gis. |
|
|
Strategic Planning |
0,594 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Strategic Analysis |
0,833 |
10 |
0,036 |
|
Strategic Direction |
0,594 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Strategic Formulation |
0,640 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Organizational Culture |
0509 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Implication |
0,532 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Consistency |
0,509 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Adaptability |
0,640 |
10 |
0,000 |
|
Mission |
0,650 |
10 |
0,000 |
Statistical inference
Analysis of the General Hypothesis:
· : Strategic planning is not significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
· : Strategic planning is significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
|
Table 12. Correlation statistics between strategic planning and organizational culture |
|||
|
|
Strategic Planning |
||
|
|
Organizational Culture |
Correlation coefficient |
0,764* |
|
Rho of Spearman |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
0,010 |
|
|
|
N |
10 |
|
**. The correlation is significant at level 0.05 (bilateral) |
|||
According to table No. 12, Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and organizational culture, whose correlation coefficient is 0,764, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,010 which is less than 0,05 (5 %), therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, this means that: strategic planning is significantly associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Analysis of Specific Hypotheses
Specific Hypothesis 1:
· : Strategic planning is not significantly associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
· : Strategic planning is significantly associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
|
Table 13. Correlation statistics between strategic planning and company involvement |
|||
|
|
Strategic Planning |
||
|
|
Company Involvement |
Correlation coefficient |
0.759** |
|
Rho of Spearman |
|
Sig. (bilateral) |
0,011 |
|
|
|
N |
10 |
|
**. The correlation is significant at level 0.05 (bilateral). |
|||
According to table No. 13, Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and involvement of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,759, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a considerable positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,011 which is less than 0,05 (5 %), therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, this means that: Strategic planning is significantly associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Specific Hypothesis 2:
· : Strategic planning is not significantly associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
· : Strategic planning is significantly associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
|
Table 14. Correlation statistic between strategic planning and enterprise consistency |
|||
|
|
Strategic Planning |
||
|
|
Company Consistency |
Correlation coefficient |
0,764** |
|
Rho of Spearman |
Sig. (bilateral) |
0,010 |
|
|
0 |
N |
10 |
|
|
**. The correlation is significant at level 0.05 (bilateral) |
|||
According to table No. 14, Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and consistency of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,764, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,010 which is less than 0,05 (5 %), therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, this means that: Strategic planning is significantly associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Specific Hypothesis 3:
· : Strategic planning is not significantly associated with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
· : Strategic planning is significantly associated with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
|
Table 15. Correlation statistics between strategic planning and company adaptability |
|||
|
|
Strategic Planning |
||
|
|
Business Adaptability |
Correlation coefficient |
0.802** |
|
Rho of Spearman |
Sig. (bilateral) |
0,005 |
|
|
|
N |
10 |
|
|
**. The correlation is significant at level 0.05 (bilateral) |
|||
According to table No. 15, Spearman’s Rho statistical test was applied for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and adaptability of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,802, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,005 which is less than 0,05 (5 %), therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, this means that: Strategic planning is significantly associated with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
Specific Hypothesis 4:
· : Strategic planning is not meaningfully associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
· : Strategic planning is significantly associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
|
Table 16. Correlation statistic between strategic planning and company mission |
|||
|
|
Strategic Planning |
||
|
|
Company Mission |
Correlation coefficient |
0,986** |
|
Rho of Spearman |
Sig. (bilateral) |
0,000 |
|
|
|
N |
10 |
|
|
**. The correlation is significant at level 0,05 (bilateral). |
|||
According to table No. 16, the Rho de Spearman statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and mission of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,986, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as perfect positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,000 which is less than 0,05 (5 %), therefore, the null hypothesis is rejected, this means that: Strategic planning is significantly associated with the mission of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. in the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021.
DISCUSSIONS
According to the results obtained, in response to the general objective: to determine how strategic planning is associated with the organizational culture of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. The existence of a significant association between both variables was evidenced. In the contrast of the general hypothesis, the Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and organizational culture, whose correlation coefficient was 0,764, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there was a p_valor = 0,010 that is less than 0,05 (5 %). Likewise, in the descriptive statistics regarding the strategic planning variable, of the total respondents, 30,0 % (n = 3) manifest a Regular Level, which indicates that the company performs strategic planning, but does not have it reflected in a plan and 70,0 % (n = 7) manifest a High Level, which indicates that the company carries out strategic planning, The same that reflects in a plan and with respect to the variable organizational culture, it has that 20,0 % (n = 2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular organizational culture and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good organizational culture. While, with respect to the organizational culture variable, 20,0 % (n = 2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular organizational culture and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good organizational culture. This research has a similarity with the work of Yanet Huallpa,(16) in the thesis of Master, Strategic Planning and Organizational Culture in Teachers of the Most Holy Name of Jesus - San Borja, 2020 that, from associative analysis and inferential statistics, achieved the common goal: to identify the relationship between PE and CO in teachers of the SNJ-San Borja Educational Institution in the year 2020, finding a strong correlation of 72,4 % between PE and CO. In addition to the variance of the general hypothesis, the level of significance p = 0,00 < 0,05 among the research variables was verified. Thus, after obtaining Rho 0,664, it was established that there is a moderate relationship between PE and CO.
Regarding the first specific objective: to determine how strategic planning is associated with the involvement of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, a significant association between the EP and involvement was perceived. In the contrast of specific hypothesis 1, the Rho de Spearman statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and involvement of the company, whose correlation coefficient was 0,759, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a considerable positive correlation, in addition there was a p_valor = 0,011, which is less than 0,05 (5 %). Similarly, in the descriptive statistics, regarding the dimension of involvement of the organizational culture variable, it was observed that 10,0 % (n = 1) manifest a low level, which indicates that the company has a bad involvement; 10,0 % (n = 1) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular involvement and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good involvement. These results agree with the research of Cuenca Galarza & López Paredes (12), who in their scientific article, study of the management of commitment and organizational culture of FLACSO, affirmed that, the commitment of employees was found in introducing people to organizational values, with a moderate correlation of 0,441, with the achievement of institutional objectives, That is, if employees didn't feel well defined, it was difficult to match organizational outcomes. They also suggested developing a corporate identity plan that would allow employees to learn about FLACSO's culture, as well as developing an accreditation plan that fosters the emotional commitment and willingness of member employees to remain in the organization.
In relation to the second specific objective: to determine how strategic planning is associated with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, a significant association between the SP and consistency was perceived. In the contrast of specific hypothesis 2, Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and consistency of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,764, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,010 that is less than 0,05 (5 %). Similarly, in the descriptive statistics, regarding the dimension consistency of the organizational culture variable, it was noted that 20,0 % (n = 2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular consistency and 80,0 % (n = 8) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good consistency. These results agree similarly with Palafox Soto et al.(13) who in their scientific article, organizational culture as a basis for permanence in organizations, conclude that organizational culture brings positive aspects, such as respecting strategies to work optimally and allows employees to adopt a strong and healthy culture, not only for work but also to instill it in their values and also in their personal culture, However, there can be negative aspects of the company if they go unnoticed because it can be detrimental to employees and their activities in the organization. In addition, if there are personal problems within the company, it is important to be public and enhance the adjustment of the organizational culture, seek to create a pleasant work environment, and allow everyone to understand what activities they should do and how they should be carried out, to achieve greater efficiency and strength to create value for customers and achieve long-term competitiveness.
For the third specific objective: to determine how strategic planning is associated with the adaptability of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, a significant association between the SP and adaptability was perceived. In the contrast of specific hypothesis 3, Spearman's Rho statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and adaptability of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,802, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as a very strong positive correlation, in addition there is a p_valor = 0,005 that is less than 0,05 (5 %). Likewise, in the descriptive statistics, regarding the adaptability dimension of the organizational culture variable, it was observed that 40,0 % (n=4) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular adaptability and 60,0 % (n=6) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good adaptability. According to the results, these resemble the research carried out by Meza Ariza & Guatibonza Tamayo,(11) who in their scientific article, organizational culture as a leverage factor of strategic planning, make a theoretical proposal of the relationship between organizational culture and strategic planning to facilitate the achievement of organizational goals, the proposal is based on the organizational culture model of Cameron and Quinn (1999) and the McKinsey 7S model of Waterman, Peters and Phillips (1980). This proposal arises in the context of a constantly changing business environment that makes it difficult for organizations to maintain stability and, sometimes, keep pace with new market demands, losing positions and, in serious cases, disappearing due to threats, on the growth of industries that anticipated and adopted strategies to ensure their survival.
In what corresponds to the fourth specific objective: to determine how strategic planning is associated with the mission of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021, a significant association between the EP and the mission was perceived. In the contrast of specific hypothesis 4, the Rho de Spearman statistical test was applied, for the analysis of the association between strategic planning and mission of the company, whose correlation coefficient is 0,986, which according to the correlation analysis table is considered as perfect positive correlation, in addition there was a p_valor = 0,000 that is less than 0,05 (5 %). In the same sense, in the descriptive statistics, regarding the mission dimension of the organizational culture variable, it is necessary that 10,0 % (n = 1) manifest a low level, which indicates that the company has a bad mission; 20,0 % (n = 2) manifest a regular level, which indicates that the company has a regular mission and 70,1 % (n = 7) manifest a high level, which indicates that the company has a good mission. Among other research that resembles is that of Alarcón Aburto,(23) who in his undergraduate thesis, Strategic Planning and its Influence on the Business Development of the MSEs of Ciudad de Dios – SJM, 2018, points out that the results obtained by hypothesis testing and statistical analysis, result in Pearson's correlation and linear regression tests that indicate that there is a very strong positive relationship between both variables. The correlation 0,932 concludes that there is an effect between strategic planning and business development. Therefore, strategic planning contributes 96,9 % to the growth of the MSE business. In terms of: the organization's mission, the organization's vision, and the organization's business development goals, it has been found to have a significant impact 2018.
CONCLUSIONS
· In relation to the general objective, it was possible to determine the association of strategic planning (PE) with the organizational culture (CO) of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. Based on the results obtained (p=0,010; Rho=0,764) it was concluded that there is a very strong positive correlation between PE and OC; that is, as there is a better PE there will be a better CO in the company.
· Regarding specific objective 1, it was possible to determine the association of the EP with the involvement of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. Based on the results obtained (p=0,011; Rho=0,759) it was concluded that there is a considerable positive correlation between the SP and the involvement; that is, as there is a better EP there will be greater involvement in the company.
· Regarding specific objective 2, it was possible to determine the association of the EP with the consistency of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. Based on the results obtained (p=0,010; Rho=0,764) it was concluded that there is a very strong positive correlation between PE and consistency; that is, as there is a better PE there will be better consistency in the company.
· Regarding specific objective 3, it was possible to determine the association of the EP with the adaptability of Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. Based on the results obtained (p=0,005; Rho=0,802) it was concluded that there is a very strong positive correlation between PE and adaptability; that is, as there is a better PE there will be a better adaptability in the company.
· Regarding specific objective 4, it was possible to determine the association of the EP with the mission of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C. of the district of Lunahuaná - Cañete 2021. Based on the results obtained (p=0,000; Rho=0,986) it was concluded that there is a perfect positive correlation between the EP and the mission, that is, that as there is a better PE there will be a better mission in the company.
REFERENCES
1. Villarán de la Puente F. El mundo de la pequeña empresa [Internet]. 1ra ed. Lima - Perú: Ministerio de Comercio Exterior y Turismo; 2007 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–336 p. Available from: https://books.google.com.pe/books/about/El_mundo_de_la_peque%C3%B1a_empresa.html?id=RvW6AAAAIAAJ&redir_esc=y
2. Beltrán A. Los 20 problemas de la pequeña y mediana empresa. G. Balint, Antala B, Carty C, Mabieme JMA, Amar IB, Kaplanova A, editors. Sotavento MBA [Internet]. 2006 Jun 12 [cited 2023 Sep 25];7(1):8–15. Available from: https://revistas.uexternado.edu.co/index.php/sotavento/article/view/1574
3. Cuadra S. Nicaragua, enfoque estratégico de las PYMEs en un mundo globalizado. Encuentro [Internet]. 2006 Jul 12 [cited 2023 Oct 8];(74):40–52. Available from: https://camjol.info/index.php/ENCUENTRO/article/view/3710
4. Huilcapi Masacón NÚ, Troya Terranova KT, Ocampo Ulloa WL. Impacto del COVID-19 en la planeación estratégica de las pymes ecuatorianas. RECIMUNDO [Internet]. 2020 Jul 8 [cited 2023 Oct 8];4(3):76–85. Available from: https://recimundo.com/index.php/es/article/view/851/1552
5. Noreña D. Diario Gestión. 2019 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. El futuro de las MYPES. Available from: https://gestion.pe/blog/el-arte-de-emprender-y-fallar/2019/01/el-futuro-de-las-mypes.html/?ref=gesr
6. García Paredes J, Coronado Espinoza JJ. Planeamiento estratégico aplicado a las micro y pequeñas empresas en la Región Lima-Provincias, 2016. Big Bang Faustiniano [Internet]. 2018 Sep 30 [cited 2023 Oct 8];7(3):35–40. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348331374_Planeamiento_estrategico_aplicado_a_las_micro_y_pequenas_empresas_en_la_Region_Lima-Provincias_2016
7. Ministerio de Trabajo y Promoción del Empleo. Relación de Empresas Acreditadas de enero a diciembre 2017 [Internet]. Lima - Perú|; 2017 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://www2.trabajo.gob.pe/archivos/dnpefp/remype/2018/Remype_fa_150520118.pdf
8. Quispe chuchon J. Propuesta de mejora en la gerencia estratégica para la gestión de calidad de las micro y pequeñas empresas del sector comercio, rubro abarrotes, caso: “Bodega Sueng”, Cañete – 2019. [Internet]. Universidad Católica Los Ángeles de Chimbote. [Cañete - Perú]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad Católica Los Angeles Chimbote; 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://repositorio.uladech.edu.pe/handle/20.500.13032/17129
9. Baena Paz GME. Metodología de la Investigación [Internet]. 1ra ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: Grupo Editorial Patria; 2014 [cited 2023 Sep 25]. 1–157 p. Available from: https://books.google.com.pe/s?id=6aCEBgAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&dq=tipos+de+investigaci%C3%B3n&hl=es&sa=X&ved=2ahUKEwjXrbeurtzxAhWBJ7kGHampAkgQ6AEwAXoECAYQAg#v=onepage&q=tipos%20de%20investigaci%C3%B3n&f=false
10. Gómez Zuluaga ME. Emprendimiento de base tecnológica: Un reto por cumplir. Tec Empresarial [Internet]. 2019 May 1 [cited 2023 Oct 8];13(2):33–44. Available from: http://www.scielo.sa.cr/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1659-33592019000200033&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=es
11. Meza Ariza LC, Guatibonza Tamayo CM. La Cultura organizacional como factor apalancador de la planeación estratégica. Revista de Investigaciones [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8];6(1):46–59. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/318381236_La_Cultura_organizacional_como_factor_apalancador_de_la_planeacion_estrategica
12. Cuenca Galarza RX, López Paredes HA. Estudio de la Gestión del Compromiso y Cultura Organizacional de FLACSO. PODIUM [Internet]. 2020 Jun 25 [cited 2023 Oct 8];37(37):43–56. Available from: https://revistas.uees.edu.ec/index.php/Podium/article/view/433
13. Palafox Soto MO, Ochoa Jiménez S, Jacobo Hernández CA. Organizational culture as a basis for the permanence of organizations. Revista San Gregorio [Internet]. 2019 Dec 29 [cited 2023 Oct 8];1(35):198–207. Available from: http://scielo.senescyt.gob.ec/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S2528-79072019000200198&lng=en&nrm=iso&tlng=es
14. Ayres Farina LS, Rodrigues G dos R, Hutz CS. Flow and engagement at work: A literature review. Psico-USF [Internet]. 2018 Oct 1 [cited 2023 Sep 25];23(4):633–42. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/329407962_Flow_and_Engagement_at_Work_A_Literature_Review
15. Llana AJO, Ruiz JAZ, Claudio BAM. Quality of service and citizen satisfaction in a Lima district municipality. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:17–17. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202317
16. Viera EJH, Meléndez NMN, Claudio MCM, Ruiz JAZ. Selection process in the Operations area of a company in the ecological sector. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:13–13. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202313.
17. Olugbola SA. Exploring entrepreneurial readiness of youth and startup success components: Entrepreneurship training as a moderator. Journal of Innovation & Knowledge. 2017 Sep 1;2(3):155–71.
18. Yanet Huallpa E. Planeamiento estratégico y cultura organizacional en los docentes de la Institución Educativa Santísimo Nombre de Jesús - San Borja, 2020 [Internet]. Repositorio Institucional - UCV. [Lima - Peru]: Tesis de Maestria - Universidad Cesar Vallejo; 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://repositorio.ucv.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12692/50613
19. Ore H, Olortegui E, Ponce D. Planeamiento estratégico como instrumento de gestión en las empresas: Revisión bibliográfica. Revista Científica Pakamuros. 2020 Dec 30;8(4):31–44.
20. Llontop Herrera CY. Planeación estratégica en las micro y pequeñas empresas en el Perú [Internet]. Universidad Nacional Toribio Rodríguez de Mendoza - UNTRM. [Chachapoya - Peru]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad Nacional Toribio Rodriguez de Mendoza de Amazonas; 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://repositorio.untrm.edu.pe/handle/20.500.14077/2320
21. Ataucusi Catay LM. Planeamiento Estratégico y Gestión Empresarial del Centro Comercial Mega Centro 1040 en el año 2018 [Internet]. Universidad Peruana Los Andes. [Huancayo - Peru]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad Peruana Los Andes; 2019 [cited 2023 Sep 25]. Available from: http://repositorio.upla.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12848/1154
22. Silva Borja GP. Planeamiento estratégico y la gestión administrativa de la Unidad de Nivelación y Admisión, “Universidad Nacional de Chimborazo”, ciudad de Riobamba- “Ecuador” [Internet]. [Lima - Perú]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad Nacional Mayor de San Marcos; 2019 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/323351138.pdf
23. Carranza Lagos JM, Garcia Serra M, Portuguez Luyo J, Santiago Chavez CA. Plan de marketing para la bodega Santa Maria: Jolly Roger [Internet]. [Lima - Peru]: Tesis de Maestría - Universidad San Ignacio de Loyola; 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 4]. Available from: https://repositorio.usil.edu.pe/server/api/core/bitstreams/ceb95536-0e01-4d14-91f0-d2912941bd9d/content
24. Dionicio RJA, Serna YPO, Claudio BAM, Ruiz JAZ. Sales processes of the consultants of a company in the bakery industry. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:2–2. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa20232.
25. Velásquez AA, Gómez JAY, Claudio BAM, Ruiz JAZ. Soft skills and the labor market insertion of students in the last cycles of administration at a university in northern Lima. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2024;2:21–21. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202421.
26. Díaz Inca JV. Planeamiento estratégico y gestión financiera en las Mypes comercializadoras de lima metropolitana, periodos 2015-2016 [Internet]. [Lima - Peru]: Tesis de Maestria - Universidad Nacional Federico Villareal; 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://alicia.concytec.gob.pe/vufind/Record/RUNF_55555c5d46f56b10554523eba36ead86
27. Alarcón Aburto AD. La planeación estratégica y su influencia en el desarrollo empresarial de las Mypes de Ciudad de Dios – SJM, 2018 [Internet]. Universidad César Vallejo. [Lima - Peru]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad César Vallejo; 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 9]. Available from: https://repositorio.ucv.edu.pe/handle/20.500.12692/19383
28. Goicochea Centeno ZB. Propuesta de mejora de la planeación estrategica para la gestion de calidad de las micro y pequeñas empresas del sector servicio, rubro restaurante, caso: La isla del sabor, imperial - Cañete, 2019 [Internet]. [Cañete - Peru]: Tesis de Licenciatura - Universidad Catolica Los Angeles Chimbote; 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Available from: https://repositorio.uladech.edu.pe/bitstream/handle/20.500.13032/18910/GESTI%C3%93N_CALIDAD_MYPES_PLANEACI%C3%93N_ESTRAT%C3%89GICA_RESTAURANTE_GOICOCHEA_CENTENO_ZORINA_BETSCY.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y
29. Chiavenato I. Administración de recursos humanos [Internet]. 9na ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: McGRAW-HILL/INTERAMERICANA EDITORES, S.A. DE C.V.; 2011 [cited 2023 Oct 4]. 1–442 p. Available from: https://www.sijufor.org/uploads/1/2/0/5/120589378/administracion_de_recursos_humanos_-_chiavenato.pdf
30. Naranjo Pérez R, Mesa Espinosa MA, Solera Salas J. De la administración por objetivos al control estratégico. Tecnología en Marcha [Internet]. 2005 [cited 2023 Oct 8];18(1):57–65. Available from: https://dialnet.unirioja.es/servlet/articulo?codigo=4835876&info=resumen&idioma=SPA
31. Asturias Corporación Universitaria. Administración por Objetivos (APO) [Internet]. 2019 [cited 2023 Sep 25]. Available from: https://www.centro-virtual.com/recursos/biblioteca/pdf/procesos_th_administrativas/unidad3_pdf2.pdf
32. Chiavenato I. Introducción a la teoria general de la administracion [Internet]. 7ma ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: McGRAW-HILL/ÍNTER AMERICAN A EDITORES, S.A. DE C.V.; 2006 [cited 2023 Oct 4]. 1–589 p. Available from: https://frrq.cvg.utn.edu.ar/pluginfile.php/15525/mod_resource/content/0/Chiavenato%20Idalverto.%20Introducci%C3%B3n%20a%20la%20teor%C3%ADa%20general%20de%20la%20Administraci%C3%B3n.pdf
33. Calle Gómez MA, Gurumendi Espana IE, Calle Prado MA. Planeación estratégica aplicada a profesionales de la medicina y la jurisprudencia. Revista Universidad y Sociedad [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2023 Oct 4];12(3):83–9. Available from: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_abstract&pid=S2218-36202020000300083
34. Gómez Díaz CF, Rodriguez Ortiz JK. Teorias de la cultura organizacional. Revista Contabilidad y Auditoria [Internet]. 2013 [cited 2023 Oct 8];115–40. Available from: https://strathprints.strath.ac.uk/7361/
35. Contreras Cueva AB, Gómez Gómez A. Aplicación de los Cuestionarios de Denison para determinar las características de la Cultura Organizacional. Revista de Investigacion Sigma [Internet]. 2018 [cited 2023 Oct 9];5(1):59–86. Available from: https://journal.espe.edu.ec/ojs/index.php/Sigma/article/view/1204/859
36. Fernandez Collado C, Baptista Lucio P. Metodología de la Investigación [Internet]. 6ta ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: McGRAW-HILL/ INTERAMERICANA EDITORES, S.A. DE C.V.; 2014 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–632 p. Available from: https://www.esup.edu.pe/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/2.%20Hernandez,%20Fernandez%20y%20Baptista-Metodolog%C3%ADa%20Investigacion%20Cientifica%206ta%20ed.pdf
37. Godoy E. Cómo Hacer una Tesis [Internet]. 1ra ed. Buenos Aires - Argentina: Valletta Ediciones SRL; 2012 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–110 p. Available from: https://books.google.com/books/about/C%C3%B3mo_hacer_una_Tesis.html?hl=es&id=7zw0nQAACAAJ
38. Frank M, Ricci E. Education for sustainability: Transforming school curricula. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:3–3. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa20233.
39. Salazar GCL, Medina MFM, Claudio BAM, Ruiz JAZ. Product quality and profitability at masisa. Southern Perspective / Perspectiva Austral 2023;1:14–14. https://doi.org/10.56294/pa202314.
40. Morlote Samperio Norma, Celiseo Santamaría R. Metodología de la Investigación: Cuaderno de Trabajo [Internet]. 1ra ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: McGraw-Hill Interamericana Editores, S.A.; 2004 [cited 2023 Oct 9]. 1–120 p. Available from: http://librodigital.sangregorio.edu.ec/opac_css/index.php?lvl=notice_display&id=9522
41. Niño Rojas VMi. Metodología de la investigación [Internet]. 1ra ed. Bogota - Colombia: Ediciones de la u; 2011 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–158 p. Available from: https://gc.scalahed.com/recursos/files/r161r/w24802w/Nino-Rojas-Victor-Miguel_Metodologia-de-la-Investigacion_Diseno-y-ejecucion_2011.pdf
42. Del Cid A, Méndez R, Sandoval F. Investigación. Fundamentos y metodología [Internet]. 2da ed. Ciudad de Mexico - Mexico: Pearson Educacion; 2011 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–235 p. Available from: https://josedominguezblog.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/investigacion-fundamentos-y-metodologia.pdf
43. García Manjón JVicente. Gestión de la innovación empresarial : claves para ser una empresa innovadora [Internet]. 1ra ed. Madrid - España: Netbiblo; 2009 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–128 p. Available from: https://books.google.com/books/about/Gesti%C3%B3n_de_la_innovaci%C3%B3n_empresarial.html?hl=es&id=PDG6ygAACAAJ
44. Moreno Galindo E. Blogger. 2016 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. Metodología de investigación, pautas para hacer Tesis. Available from: https://tesis-investigacion-cientifica.blogspot.com/2016/12/niveles-de-investigacion-cientifica.html
45. Guisande Gonzalez C, Vaamonde Liste A, Barreiro Felpeto A. Tratamiento de datos con R, Statistica y SPSS [Internet]. 1ra ed. Madrid - España: Ediciones Diaz de Santos; 2013 [cited 2023 Oct 8]. 1–997 p. Available from: https://blog.utp.edu.co/estadistica/files/2017/09/TRATAMIENTO-DE-DATOS-CON-R-ESTATISTICA-Y-SPSS.pdf
RECOMMENDATIONS
· It is recommended that the owners of the Santa María S.A.C Winery and Vineyards in the district of Lunahuaná – Cañete encourage the development of strategic thinking that allows them to make the vision of the company their own and at the same time, help them forge an adequate solid culture within the organization.
· It is recommended that the administrators of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C, implement a strategic plan (general and / or by area), which contemplates fundamental aspects of the company such as the vision, mission, objectives, values, policies, strategic planning tools (SWOT, 7 S of Mackenzy, 5 Forces of Porter, Balance Score Card, Canvas), among other important aspects; that serve as an action guide for decision making, Likewise, socialize the plan with all the members of the company, in order to identify and generate commitment to comply with the planned in the short, medium and long term, in a shared manner. In the same way, it is necessary to evaluate the fulfillment of the strategic planning that is designed, to apply the improvements that are required, satisfying the expectations of both internal and external clients of the organization.
· It is recommended to the collaborators of the Bodega y Viñedos Santa María S.A.C, contribute with their participation and opinion when establishing the organizational objectives, since they are a fundamental part of the company and must feel involved with an organization that trusts in their work to achieve business success.
· It is recommended that the competent public institutions, the Ministry of Labor, and Municipalities, encourage free campaigns on strategic business planning, publicizing the benefits and importance of planning strategies for the development of MSEs.
· It is recommended that companies in the province of Cañete have specialized advice on strategic business planning, which allows them to formalize the plans and carry out the constant evaluation of compliance with them.
· It is recommended to Micro and Small Enterprises, develop strategies that allow them to increase their competitiveness, position themselves in the market, enhance their brand and most importantly minimize risks.
· It is recommended that other researchers take as background the present research, which concludes that there is a very strong positive correlation between strategic planning and organizational culture, from which research can be generated that helps improve the competitiveness of Micro and Small Enterprises in the Province of Cañete, such an important sector in the national economy.
· It should be noted that strategic planning does not ensure the solution to all the problems that a company may present, however, it is an excellent management tool that allows us to reduce risks and be better prepared for any situation, facilitating decision making and providing multiple benefits, if used properly and trying to unify efforts for compliance.
FINANCING
The authors did not receive financing for the development of this research.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
AUTHORSHIP CONTRIBUTION
Conceptualization: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Alberto Ramón-Osorio, Segundo Ríos-Ríos, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez.
Data curation: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Alberto Ramón-Osorio.
Formal analysis: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco.
Acquisition of funds: No funds.
Research: Miguel Vargas-Tasayco, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez.
Methodology: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco.
Project management: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Miguel Vargas-Tasayco.
Resources: Miguel Vargas-Tasayco, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez.
Software: Miguel Vargas-Tasayco, Yrene Uribe-Hernandez.
Supervision: Alberto Ramón-Osorio, Segundo Ríos-Ríos.
Validation: Alberto Ramón-Osorio, Segundo Ríos-Ríos.
Display: Segundo Ríos-Ríos.
Drafting - original draft: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Alberto Ramón-Osorio.
Writing - proofreading and editing: Ana Chaman-Bardalez, Alberto Ramón-Osorio.